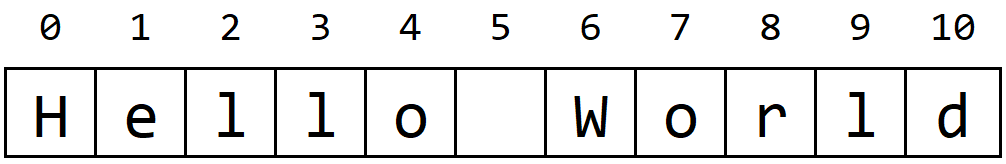Using ASCII, we can now store and manipulate text in our programs. There are a couple of different ways our programs store and interact with text, so let’s cover both of them here before moving on.
Characters
In programming, the smallest piece of text is referred to as a character. We sometimes use the term letter to refer to the smallest parts of text, since a word in text is made up of many letters, but technically symbols such as &, ( and # are not letters, so we should refer to them as characters instead. This helps avoid any confusion.
A character, therefore, is a single symbol in written text. Using ASCII, it would represent a single entry on that table, so it could be stored as a single integer in a computer.
In fact, many programming languages include a special data type for storing characters, sometimes referred to as the char data type. This is really handy if we need to store a single character of text, or want to convert between the character’s textual value and the underlying number used in ASCII to store the character.
Typically, single characters are denoted using a single quotation mark, both in code and when written. So, the first character of the alphabet would be written as 'a' or 'A'.
Strings
So, how can we store larger pieces of text, such as words and sentences? In a programming language, we refer to these longer pieces of text as strings. So, a string can refer to any text stored in a computer. Most programming languages also include a specific data type named String, just for storing and interacting with strings of text. We’ll learn all about how to use these data types in this chapter. Strings are usually written inside of double quotation marks. We’ve already seen examples of this, such as “Hello World” in our very first program.
So, what is a string? In essence, a string is just an an aggregation of characters, like an array or list, with each character representing one symbol in the text stored in the string.
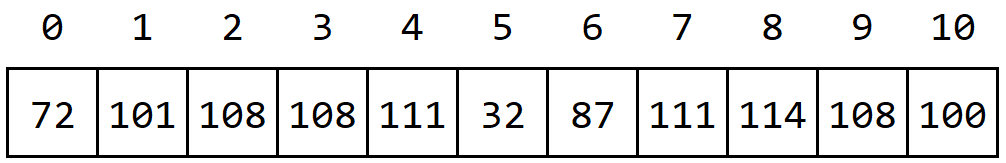
The image above shows how the text “Hello World” would be stored on our computer as a string. It is simply an array of characters, with each character representing a single symbol from the text, stored in order. As we learn more about using strings in our programs, we’ll see how useful it is to know that each character in the string has an index, just like elements in an array.
Behind the scenes, our computer is actually storing the numerical value for each character, so it would actually be seeing these values. However, by using special data types for storing text as strings, it will display the characters for us instead of the numbers. This is why it is important for our programming languages to have different data types: it allows us to store all of our data as numbers, specifically binary numbers, and the programming language uses the data type to tell the computer how to interpret that data when we use it in our programs. Pretty neat, right?