To search for a single number in our array, we will use a loop to search each location in the array until we find the number. The general idea is to iterate over all the elements in the array until we either find the number we are searching for or there are no other elements in the array.
1function FIND(NUMBER, ARRAY)
2 loop INDEX from 0 to size of ARRAY - 1
3 if ARRAY[INDEX] == NUMBER
4 return INDEX
5 end if
6 end for
7 return -1
8end functionAs we can see in line 1, the function takes both a number and array parameter. We then enter a for loop in line 2 to loop through each location in the array. We keep track of the current location in the array using the index variable. For each location, we compare number against the value in the array at location index. If we find the number, we simply return the value of index in line 4. If we do not find the number anywhere in the array, the loop will exit, and the function will return -1 in line 8.
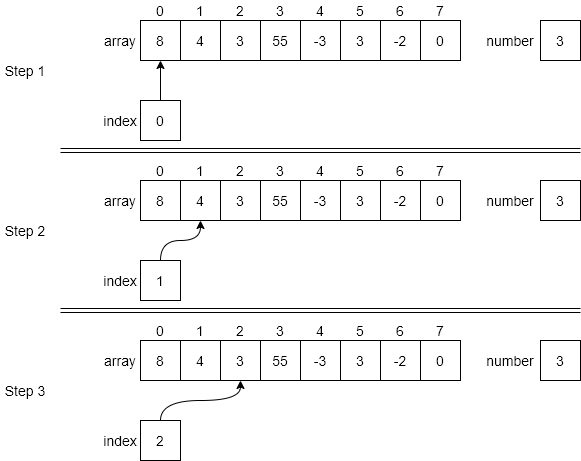
Below is an example of how to execute this algorithm on example data. Step 1 shows the initial state of the variables in the function the first time through the loop. Both array and number are passed to the function but we do not modify either of them in the function. The index variable is the for loop variable, which is initially set to 0 the first time through the loop. In line 3, the function compares the number in array[index] against the value of number. In this step, since index is 0, we use array[0], which is 8. Since 8 is not equal to the value of number, which is 3, we do nothing in the if statement and fall to the end for statement in line 6. Of course, this just sends us back to the for statement in line 2.
The second time through the for loop is shown as Step 2 in the figure. We follow the same logic as above and compare array[1], or 4, against number, which is still 3. Since these values are not equal, we skip the rest of the if statement and move on to Step 3.
In Step 3, index is incremented to 2, thus pointing at array[2], whose value is 3. Since this value is equal to the value of number, we carry out the if part of the statement. Line 4 returns the value of 2, which is the first location in array that holds the value of number.