General Terms
To get ourselves comfortable in working with trees, we will outline some standard vocabulary. Throughout this section, we will use the following tree as a guiding example for visualizing the definitions.
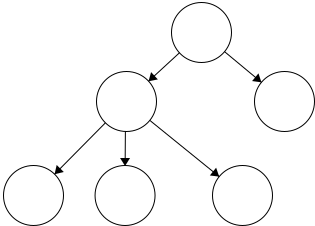

Definitions
Node- the general term for a structure which contains an item, such as a character or even another data structure.Edge- the connection between two nodes. In a tree, the edge will be pointing in a downward direction.
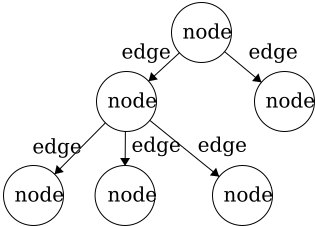
 This tree has five edges and six nodes. There is no limit to the number of nodes in a tree. The only stipulation is that the tree is
This tree has five edges and six nodes. There is no limit to the number of nodes in a tree. The only stipulation is that the tree is fully connected. This means that there cannot be disjoint portions of the tree. We will look at examples in the next section.
A rule of thumb for discerning trees is this: if you imagine holding the tree up by the root and gravity took effect, then all edges must be pointing downward. If an edge is pointing upward, we will have a cycle within our structure so it will not be a tree.
Root- the topmost node of the tree
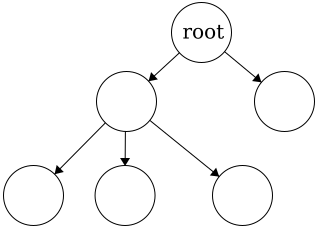
 To be a tree, there must be exactly one root. Having multiple roots, will result in a
To be a tree, there must be exactly one root. Having multiple roots, will result in a cycle or a tree that is not fully connected. In short, a cycle is a loop in the tree.
Parent- a node with an edge that connects to another node further from the root. We can also define the root of a tree with respect to this definition;Root: a node with no parent.Child- a node with an edge that connects to another node closer to the root.- In a general tree, the children of a node are an unordered set. There is not a fixed or defined order for generic trees.
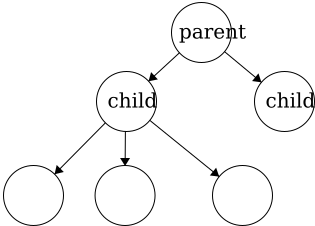

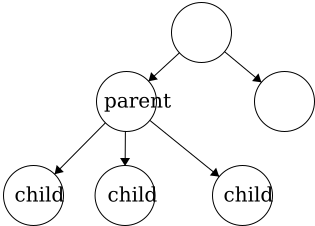
 In a tree, child nodes must have exactly one parent node. If a child node has more than one parent, then a
In a tree, child nodes must have exactly one parent node. If a child node has more than one parent, then a cyclewill occur. If there is a node without a parent node, then this is necessarily the root node. There is no limit to the number of child nodes a parent node can have, but to be a parent node, the node must have at least one child node.
- In a general tree, the children of a node are an unordered set. There is not a fixed or defined order for generic trees.
Leaf- a node with no children.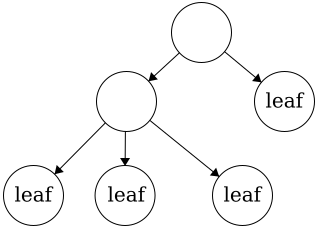
 This tree has four leaves. There is no limit to how many leaves can be in a tree.
This tree has four leaves. There is no limit to how many leaves can be in a tree.
DegreeDegree of a node- the number of children a node has. The degree of a leaf is zero.Degree of a tree- the number of children the root of the tree has.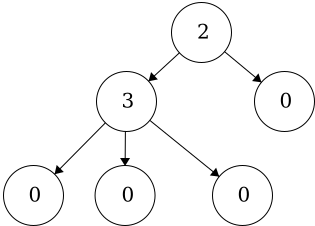
 The degree of the nodes are shown as the values on the nodes in this example. The degree of the tree is equal to the degree of the root. Thus, the degree for this tree is 2.
The degree of the nodes are shown as the values on the nodes in this example. The degree of the tree is equal to the degree of the root. Thus, the degree for this tree is 2.
- A
treeis defined recursively. This means that each child of the root is the root of another tree and the children of those are roots to trees as well. Again, this is a recursive definition so it will continue to the leaves. The leaves are also trees with just a single node as the root.
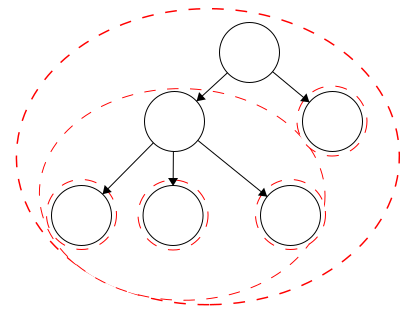
 In our example tree, we have six trees. Each tree is outlined in a red dashed circle:
In our example tree, we have six trees. Each tree is outlined in a red dashed circle:
- the main tree,
- the tree off the left of the main root,
- the tree off the left of this root,
- the tree in the center of this root,
- the tree off the right of this root, and
- the tree off the right of the main root with a single node
- the tree off the left of the main root,
- the main tree,