Fakes
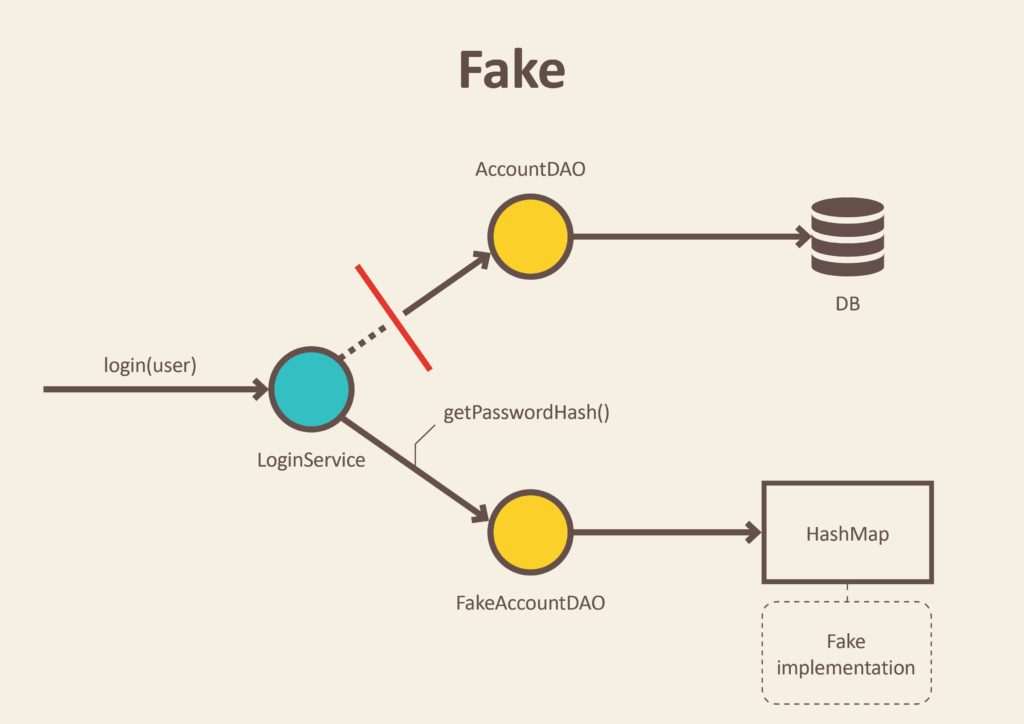
Another commonly used test double is a fake, sometimes referred to as a fake object. A fake is an object that implements the same external interface that the real object would implement - it includes all of the same publicly available methods and attributes. However, the implementations of those methods may take certain shortcuts to mimic pieces of functionality that are not really needed in order to produce valid results. (Many test frameworks use the term mock object for the same concept; however, we’ll use that term on the next page for a slightly different use.)
For example, if we have an object responsible for storing data in a database, we could create a fake version of it that can store data in a hash table instead. It will still be able to store objects and retrieve them, but instead of using a real database with millions of records, it will just store a few items in a hash table that can be reloaded for each unit test.
Likewise, if the object performs a long, complex calculation, a fake version of the object might include precomputed data that can be quickly returned without performing the computation. In that way, the data stored in the object corresponds to the results it provides, without the need to perform any costly computational steps during each unit test.