Python tkinter
Image Credit: Wikipedia
Python tkinter
- Python wrapper for Tk
- Developed in early 1990s
- Object-Oriented, Inheritable
- Change Look and Feel
- Cross-Platform
Imports
import tkinter as tk
# themed widgets
from tkinter import ttkClass Structure
class MainWindow(tk.Tk):
def __init__(self) -> None:
# create GUI
def action_performed(self, text: str) -> None:
# handle events
@staticmethod
def main(args: List[str]) -> None:
# start program
# Main Guard
if __name__ == "__main__":
MainWindow.main(sys.argv)
Layout
# Initialize the parent class
tk.Tk.__init__(self)
# Set the window size
self.minsize(width=200, height=100)
# Allow the grid to expand horizontally to fill the space
self.grid_rowconfigure(0, weight=1)
self.grid_rowconfigure(1, weight=1)
self.grid_columnconfigure(0, weight=1)Grid Geometry Manager
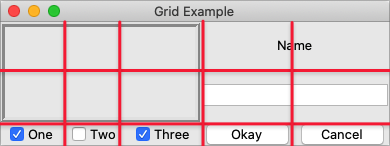
Image Credit: TkDocs
Grid Geometry Manager
Use sticky option to fill cell
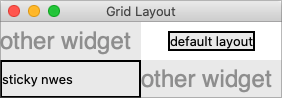
Image Credit: TkDocs
Grid Geometry Manager
Use weight option to stretch
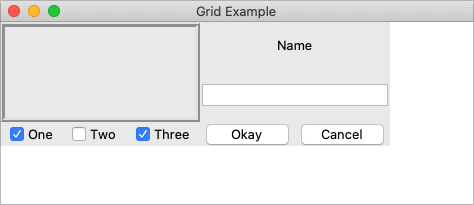
Image Credit: TkDocs
Grid Geometry Manager
Use weight option to stretch

Image Credit: TkDocs
Label
# Create a label and add it to the GUI
self.__label = tk.Label(master=self, text="Hello World!")
self.__label.grid(row=0, column=0)Button
# Create a button and add it to the GUI
self.__button = tk.Button(master=self, text="Close",
command=lambda:
self.action_performed("close"))
self.__button.grid(row=1, column=0)Python Example
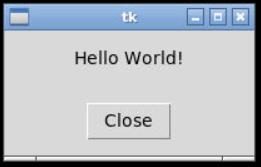
Handle Events
Specified by lambda expression
def action_performed(self, text: str) -> None:
if text == "close":
sys.exit(0)Start Application
Call the mainloop() method
@staticmethod
def main(args: List[str]) -> None:
MainWindow().mainloop()