Using VS Code
VS Code is a text editor designed for programming. You can use VS Code for lightweight development in many programming lanugages.
Opening VS Code
To open VS Code, navigate in a file explorer to the folder you wish to open (most likely, it will be cis200repo). Right click the folder and select “Open with Code”.
Alternatively, you can open VS Code as you would other applications. It will automatically open to the last folder you worked with, which will likely be cis200repo. If it is not opened to the correct folder, you can choose File->Open Folder and select your folder that way.
Disabling Copilot
GitHub Copilot is an AI tool that provides code completion. As one of the purposes of CIS 200 is to learn the fundamentals of computer programming, having an AI tool suggest code before you have a chance to think about the problem can prevent you from learning the basics. In this class, you are expected to disable the Copilot tool.
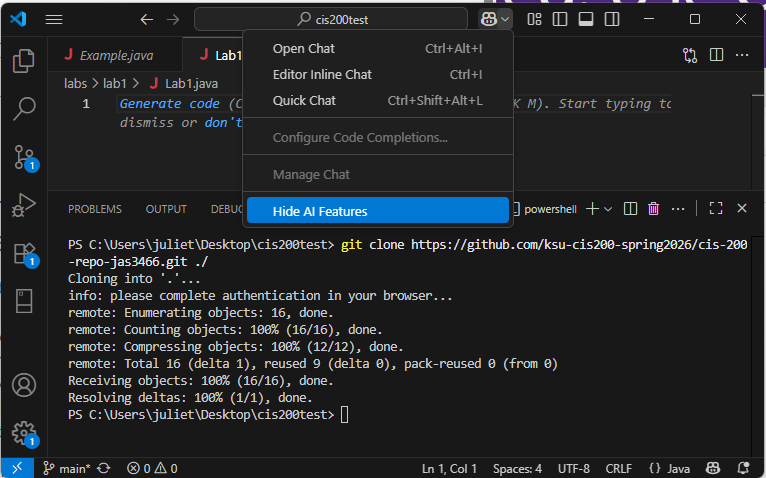
In VS Code, click the down arrow next to the Copilot icon in the top menu bar (it kind of looks like a little robot head) and select “Hide AI features”:
Confirm your choice in the following popup.
Parts of VS Code
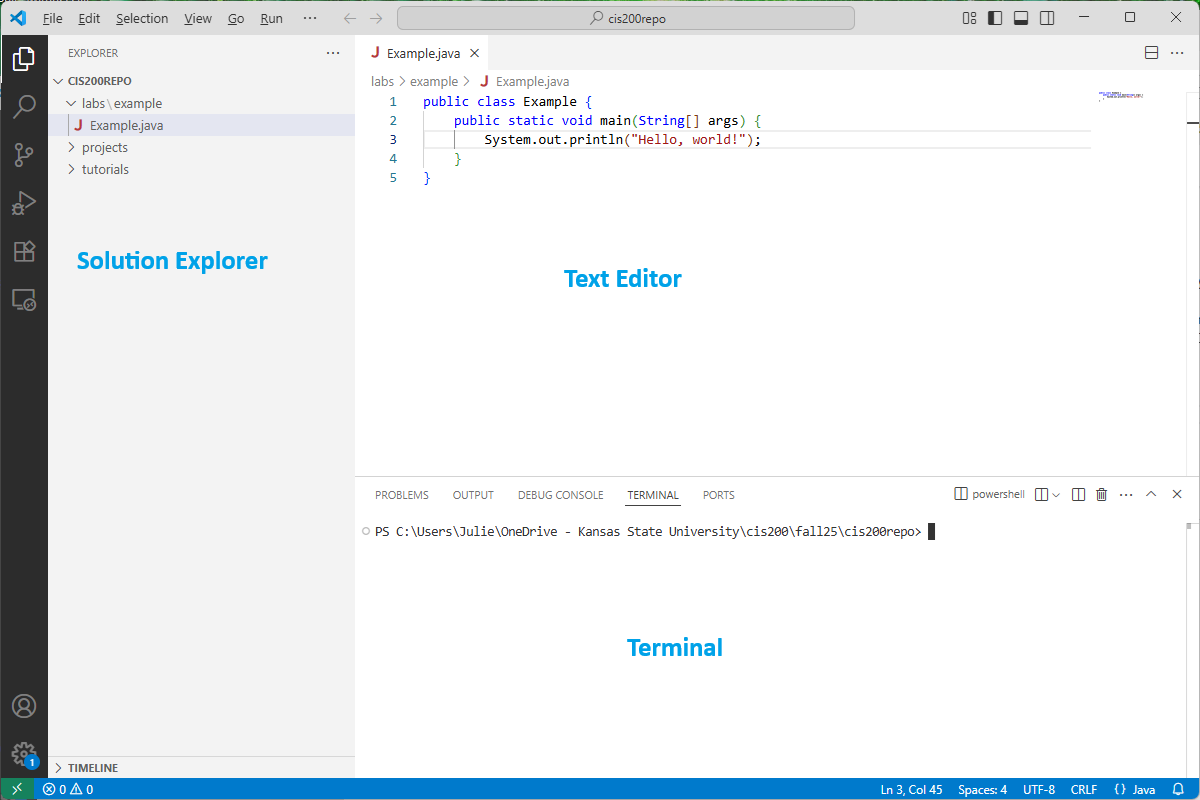
The VS Code user interface includes:
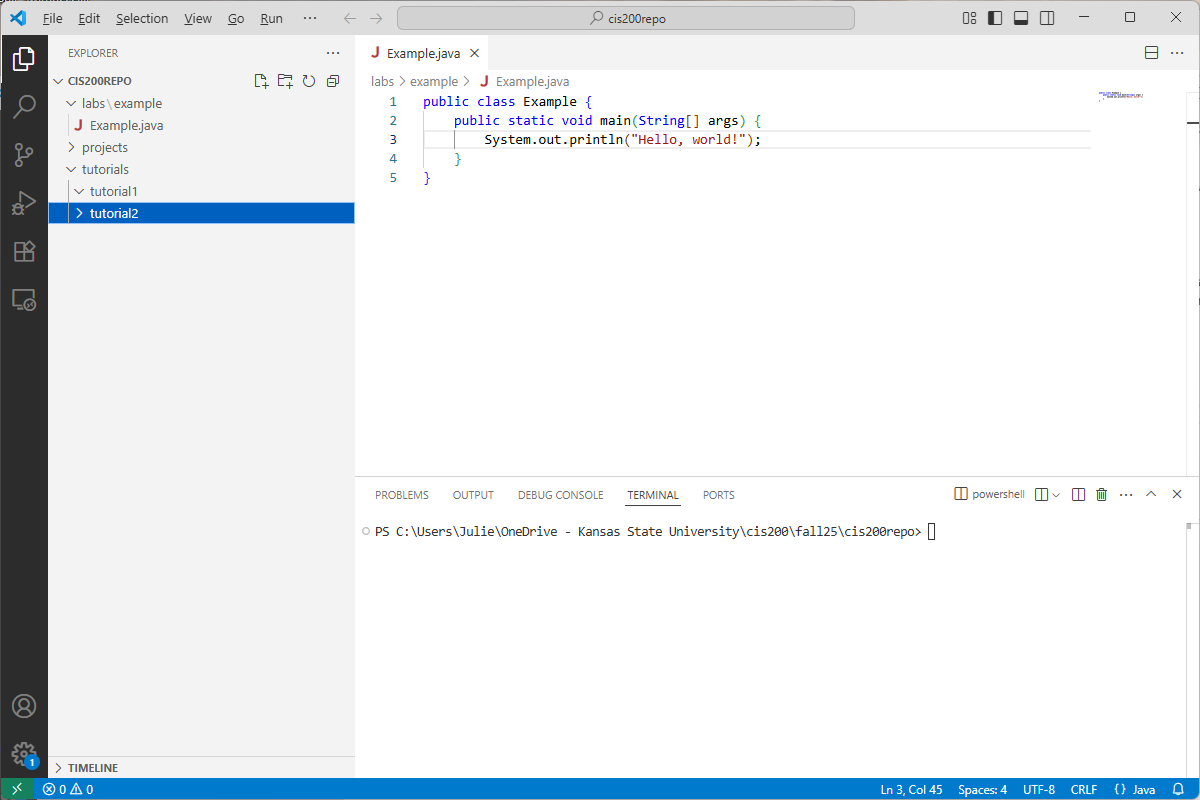
- A text editor display for a current document in the upper-right. There can be multiple document tabs open at once.
- The solution explorer on the left side, which shows all the files and subfolders within the currently open folder.
- A terminal display at the bottom, which is where we will type the instructions for compiling and running our programs. By default, the terminal opens to the same top-level folder as is opened in the solution explorer.
Here is an example:
If the solution explorer does not automatically appear, you can click the icon that looks like sheets of paper in the upper left. If the terminal doesn’t automatically appear, you can choose View->Terminal.
Creating a new subfolder
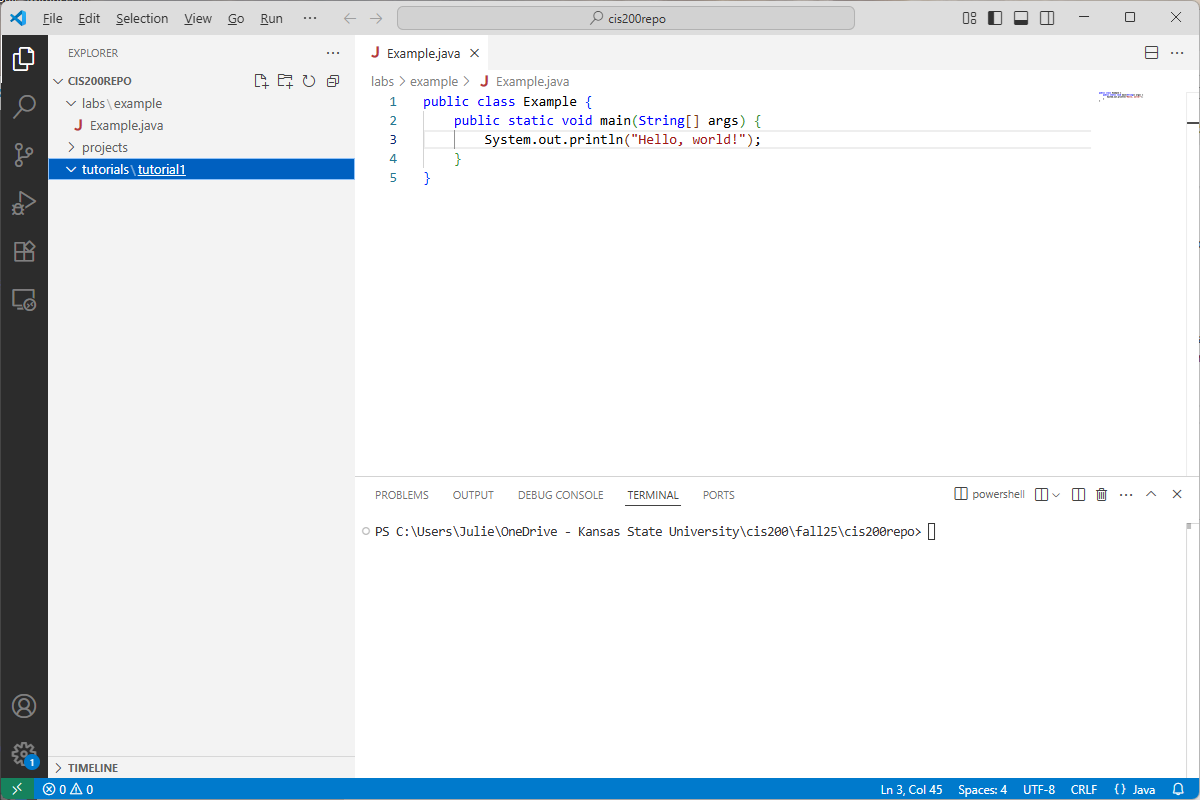
To create a new subfolder, go to the solution explorer and right-click on what you want to be the containing folder. Select “New Folder…” and enter the name of the folder. For example, I could create the tutorial1 subfolder in tutorials by entering tutorial1 as the name:
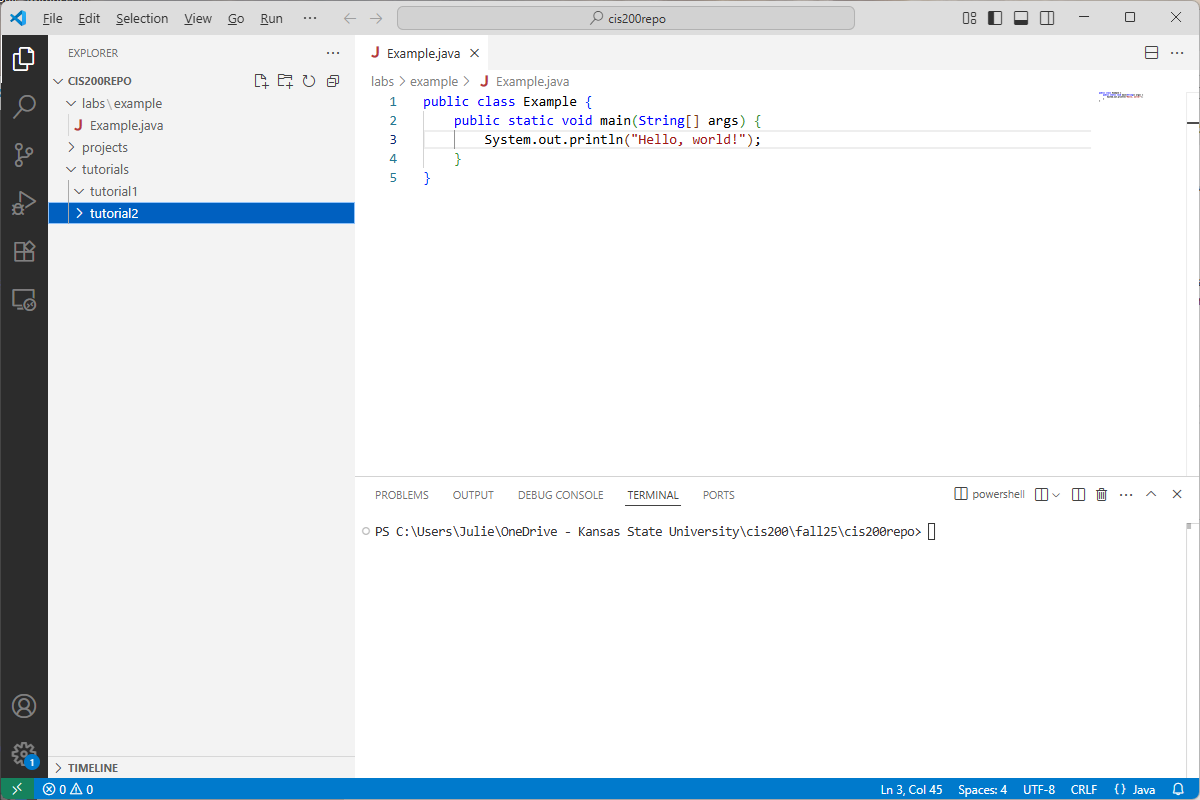
If an outer folder only contains one subfolder, then VS Code will abbreviate the display (as in tutorials\tutorial1). If I added a tutorial2 subfolder inside tutorials, it would display:
Creating a new file
To add a new file, go to the solution explorer and right-click on what you want to be the containing folder. Select “New File” and type the name of your new file (including the extension). For example, here is what I see after creating the file Tutorial1.java inside the tutorial1 folder:
Notice that the new file is opened automatically in the text editor.
Using the terminal
A side goal of this class is for students to become more comfortable with using the terminal. With practice, you will find that you are faster at navigating folders, creating files/folders, compiling/running programs, using tools stuch as git, etc. using the terminal than you are using a GUI. Familiarity with a terminal is especially useful in system administration and web development.
We will use the integrated terminal to compile and run our Java programs, as well as to add/commit/push our changes to our GitHub repository.
If the terminal isn’t already displayed at the bottom of VS Code, you can open it with View->Terminal. It will automatically open to the top-level folder in the solution explorer.
Common terminal commands
Here is a summary table of the most common terminal commands for this course:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| dir | Lists the current directory contents (only available in Windows) |
| ls | Lists the current directory contents (not available in Windows command prompt) |
| cd dirName | Changes the current directory in the terminal to be dirName. (Note: dirName must be a subfolder of the current directory.) |
| mkdir dirName | Makes a new, empty directory called dirName |
| ni fileName | Creates a new, empty file called fileName. We can do ni Test.java to create a new Java program called Test.java (only available in Windows) |
| touch fileName | Creates a new, empty file called fileName. We can do touch Test.java to create a new Java program called Test.java (only available in Mac/Linux/Unix) |
| cd .. | Updates the current directory in the terminal to be its parent directory. For example, if the current directory is C:\Users\Julie, then cd .. makes the current directory be C:\Users |
| del fileName | Deletes the file called fileName, which must be in the current directory (only available in Windows) |
| rm fileName | Deletes the file called fileName, which must be in the current directory (only available in Mac/Linux/Unix) |
Other terminal tips
When you are typing a directory name or file name in the terminal, you can type a few letters and hit Tab – the terminal will attempt to autocomplete the rest of the name.
To recall a command you recently typed in the terminal, you can use the up or down arrows. This saves you from typing the same commands over and over.
Opening the terminal to a subfolder
You can open a new terminal to a subfolder by right-clicking the folder in the solution explorer and selecting “Open in integrated terminal”.