Using git
This class will use GitHub links to create initial repositories for both labs and programming projects, similarly to what you have done in CIS 300 and 301.
GitHub account
First, you will need to create a GitHub account here. If you already have one, you can use your existing account.
Verify a git install
You will likely already have a command-line version of git installed on your machine. To check, open a folder in VS Code, display the integrated terminal, and type:
git --versionYou should see a version number printing out. If you see that, git is already installed.
If you see an error that git is unrecognized, then you will need to install it. Go here to download and install the latest version.
Windows users may need to add the git.exe location to the system Path environment variables. Most likely, git.exe will be installed to C:\Program Files\Git\bin. Check this location, copy its address, and type “Environment variables” in the Windows search. Click “Environment Variables” and find “Path” under System variables. Click “Edit…”. Verify that C:\Program Files\Git\bin (or whatever your git location) is the last item listed. If it isn’t, add a new entry for C:\Program Files\Git\bin.
Clone the repository
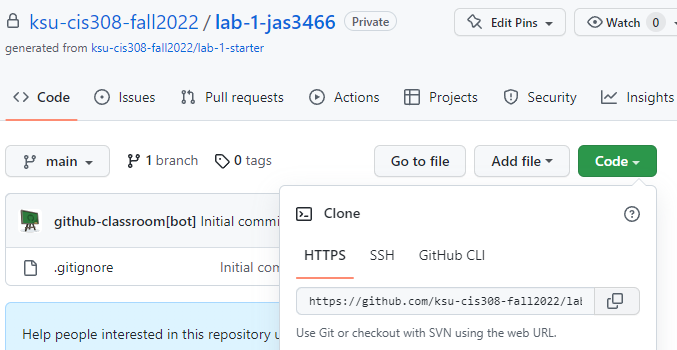
When you get a new assignment, first click the assignment link – this will create an initial GitHub repository.
After opening your GitHub repository, click the green “Code” button and click the copy icon next to the URL name. This will copy the URL of your GitHub repository:
For labs, follow the instructions under “Organizing Labs” in section 0.1 to open your CIS 308 folder in VS Code, create a new lab folder, and change directories to your empty folder.
For projects, create an empty folder on your machine, right-click the folder name, and select “Open with Code”. Then open the Terminal within VS Code by selecting “Terminal->New Terminal”. The terminal should automatically display the empty folder you just created.
Clone your GitHub repository to your new, empty folder by typing in the terminal:
git clone {repository-url} ./Where {repository-url} is the URL you copied from your GitHub repository (leave off the { and } when you insert your URL). The ./ tells git to clone the repository to the current directory.
Add code and test
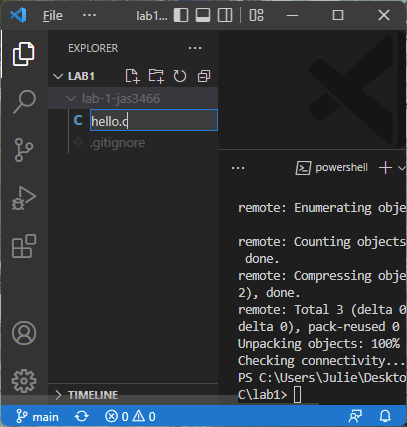
Add the necessary programming files to your project. You can add a file in VS Code by clicking your project name under “Explorer”, and then clicking the icon labeled “New File” (it looks a piece of paper with a plus sign). Type the name of your new file and hit Enter to save it:
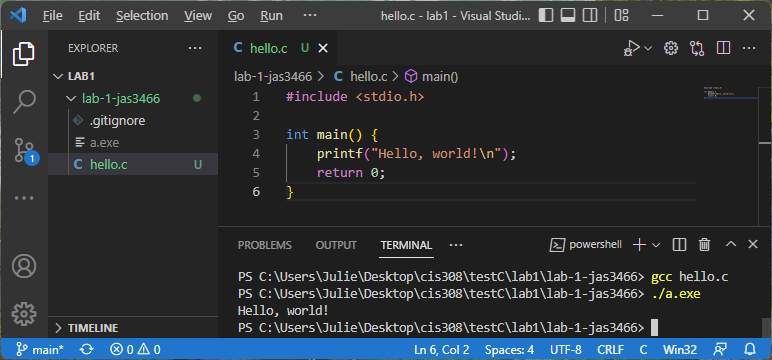
Write the code for your project. As you go, save it and test it with the gcc compiler. If it builds, run the resulting executable (either a.exe or a.out). Here is an example of compiling and running a Hello, World! program:
Commit and push
Once you are ready to commit your changes, type the following in the integrated terminal:
git add .This will add all changes to the current commit. Then type:
git commit -m "descriptive message"to create a local commit, where “descriptive message” is replaced with a message describing your changes (you DO need to include the quotations). Finally, push your local commit to the current branch:
git pushIf you go to your GitHub repository URL, you should see the latest changes.