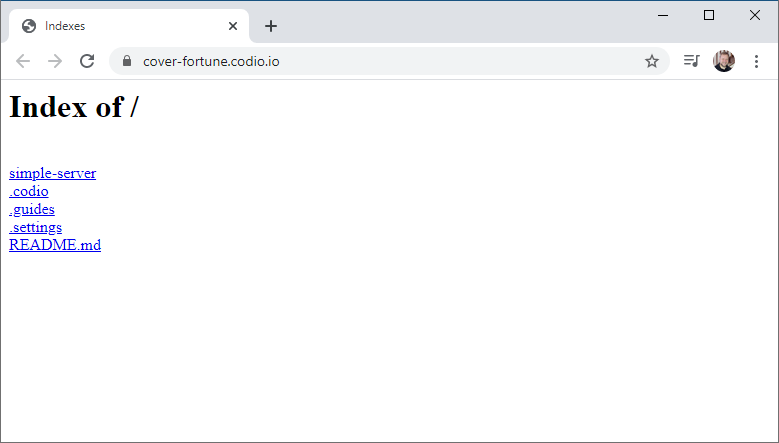
Index Pages
The original purpose of the World-Wide-Web was to share webpages and other digital resources across the Internet. In many ways, an early web server was like a hard drive that was open to the world. Think about the HTTP methods, "GET" is like a file read, "POST" is like a write, "PUT" and "PATCH" like a file modification, and "DELETE" was a file erasure.
So, just like when you browse your hard drive using Windows Explorer or other software, it was necessary for these early web pages to display an index - a listing of all the contents of a directory. You’ve seen similar in Codio if you ever used the “Project Index” option in the run menu - it displays an index of the project directory:
This is a pretty standard auto-generated directory listing - it provides the path to the directory being displayed, and all the contents of the directory as hyperlinks. Clicking on a file will open or download it, and clicking a directory will open that directory’s auto-generated directory listing.
As the use of the web expanded into commercial and public life, many web developers wanted to replace auto-generated directory listing pages with a carefully designed home page. But auto-generated directory listing pages remained an important feature for many sites that served as a more traditional file server.
The compromise adopted by most web servers was that if the directory contained an HTML file named index.html (or sometimes index with any extension, i.e. index.php), that page would be served in leu of an auto-generated index page. Most also allow disabling the directory listing as a configuration option.
Info
You might be wondering about security if a web server starts exposing directory structure and files willy-nilly. Most web servers will only serve files in a specific directory (often called the root directory) and its subdirectories. In a typical configuration, this root directory is named public or public_html to reinforce the idea that it is available to anyone browsing the web.
Files that need to have access restricted to certain people should not be placed in this directory, but be placed behind an authentication mechanism (sometimes referred to as an auth wall or pay wall for subscription-based sites). We’ll talk about this more in our chapter on authentication.