Flowcharts and Pseudocode
In this course, we will primarily be learning different ways to store and manipulate data in our programs. Of course, we could do this using the source code of our chosen programming language, but in many cases that would defeat the purpose of learning how to do it ourselves!
Instead, we will use several different ways to represent the steps required to build our programs. Let’s review a couple of them now.
Natural Language
One of the simplest ways to describe a computer program is to simply write what it does using our preferred language, such as English. Of course, natural language can be very ambiguous, so we must be careful to make our written descriptions as precise as possible. So, it is a good idea to limit ourselves to simple, clear sentences that aren’t written as prose. It may seem a bit boring, but this is the best way to make sure our intent is completely understood.
A great example is a recipe for baking. Each step is written clearly and concisely, with enough descriptive words used to allow anyone to read and follow the directions.
Flowcharts
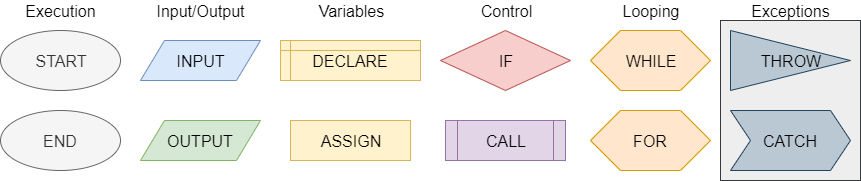
One method of representing computer programs is through the use of flowcharts. A flowchart consists of graphical blocks representing individual operations to be performed, connected with arrows which describe the flow of the program. The image above gives the basic building blocks of the flowcharts that will be used in this course. We will mostly follow the flowchart design used by the Flowgorithm program available online. The following pages in this chapter will introduce and discuss each block in detail.
Pseudocode
We can also express our computer programs through the use of pseudocode. Pseudocode is an abstract language that resembles a high-level programming language, but it is written in such a way that it can be easily understood by any programmer who is familiar with any one of several common languages. The pseudocode may not be directly executable as written, but it should contain enough detail to be easily understood and adapted to an actual programming language by a skilled programmer.
There are many standards that exist for pseudocode, each with their own unique features and uses. In this course, we will mostly follow the standards from the International Baccalaureate Organization. In the following pages in this chapter, we’ll also introduce pseudocode for each of the flowchart blocks shown above.