Comparing Data Structures
One of the best ways to compare data structures is to look at the common operations that they can perform. For this analysis, we’ve chosen to analyze the following four operations:
- Insert – inserting a specific element into the structure, either in sorted order, or at the appropriate place as required by the definition of a stack or queue.
- Access – accessing a desired element. For general data structures, this is the process of accessing an element by its index or key in the structure. For stacks and queues, this is the process of accessing the next element to be returned.
- Find – this is the process of finding a specific element in the data structure, usually by iterating through it or using a binary search method if the structure is sorted
- Delete – this is the process of deleting a specific element in the case of a general-purpose structure or deleting and returning the next element in the case of a stack or queue.
The following table compares the best- and worst-case processing time for many common data structures and operations, expressed in terms of $N$, the number of elements in the structure.
| Data Structure | Insert Best | Insert Worst | Access Best | Access Worst | Find Best | Find Worst | Delete Best | Delete Worst |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unsorted Array | $1$ | $1$ | $1$ | $1$ | $N$ | $N$ | $N$ | $N$ |
| Sorted Array | $\text{lg}(N)$ | $N$ | $1$ | $1$ | $\text{lg}(N)$ | $\text{lg}(N)$ | $\text{lg}(N)$ | $N$ |
| Array Stack (LIFO) | $1$ | $1$ | $1$ | $1$ | $N$ | $N$ | $1$ | $1$ |
| Array Queue (FIFO) | $1$ | $1$ | $1$ | $1$ | $N$ | $N$ | $1$ | $1$ |
| Unsorted Linked List | $1$ | $1$ | $N$ | $N$ | $N$ | $N$ | $N$ | $N$ |
| Sorted Linked List | $N$ | $N$ | $N$ | $N$ | $N$ | $N$ | $N$ | $N$ |
| Linked List Stack (LIFO) | $1$ | $1$ | $1$ | $1$ | $N$ | $N$ | $1$ | $1$ |
| Linked List Queue (FIFO) | $1$ | $1$ | $1$ | $1$ | $N$ | $N$ | $1$ | $1$ |
| Hash Table | $1$ | $N$ | $1$ | $N$ | $N$ | $N$ | $1$ | $N$ |
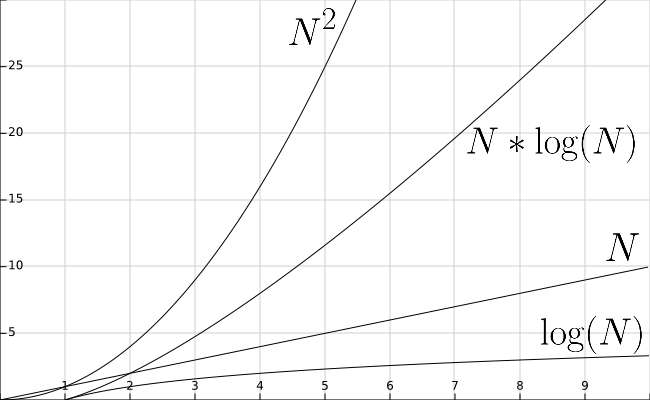
We can also compare these processing times by graphing the equations used to describe them. The graph below shows several of the common orders that we have seen so far.
On the next few pages, we will discuss each data structure in brief, using this table to compare the performance of the various data structures we’ve covered in this course.