Arrays

 ^[File:USPS Post office boxes 1.jpg. (2017, May 17). Wikimedia Commons, the free media repository. Retrieved 18:17, November 5, 2018 from https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:USPS_Post_office_boxes_1.jpg&oldid=244476438.]
^[File:USPS Post office boxes 1.jpg. (2017, May 17). Wikimedia Commons, the free media repository. Retrieved 18:17, November 5, 2018 from https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:USPS_Post_office_boxes_1.jpg&oldid=244476438.]
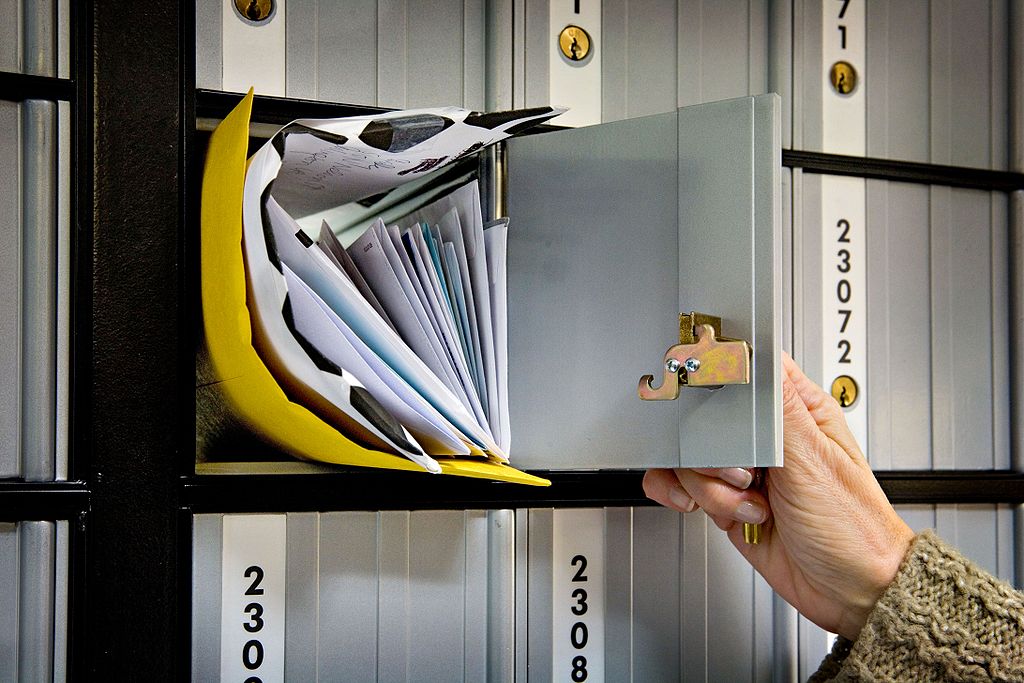
Arrays allow us to store multiple values in the same variable, using an index to determine which value we wish to store or retrieve from the array. We can think of arrays like a set of post office boxes. Each one has the same physical address, the post office, but within the post office we can find an individual box based on its own box number.
Some programming languages, such as Java, use arrays that are statically sized when they are first created, and those arrays cannot be resized later. In addition, many languages that require variables to be declared with a type only allow a single variable type to be stored in an array.
Other languages, such as Python, use lists in place of arrays. List can be resized, and in untyped languages such as Python they can store different data types within the same list.
Arrays in Flowcharts & Pseudocode
The table below lists the flowchart blocks used to represent arrays, as well as the corresponding pseudocode:
| Operation | Flowchart | Pseudocode |
|---|---|---|
| Declare Array |


|
|
| Store Item |


|
|
| Retrieve Item |
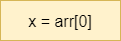
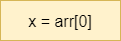
|
|
Arrays in Java
Let’s review the syntax for working with arrays in Java.
Array Creation
To declare an array in Java, we must give it a type, and a name, with square brackets [] included after the type:
Once the array is declared, we can initialize it using the new keyword, followed by the type and then the size in square brackets []:
Of course, we can combine these two statements in to a single statement as well:
Finally, if we already know the values which we want to store in the array, we can use a shortcut syntax to initialize the array and place those values directly within it:
Accessing Array Elements
Once the array is created, we can access individual items in the array by placing the index in square brackets [] after the array’s variable name:
Multidimensional Arrays
Java arrays can also be created with multiple dimensions, simply by adding additional square brackets [] to represent and access items in each dimension:
Array Operations
There are several operations that can be performed on arrays in Java as well:
Array Loops
Finally, we can use a special form of loop, called an Enhanced For loop, to iterate through items in an array in Java:
Once important thing to note is that arrays accessed within an Enhanced For loop are read only. So, we cannot change the values stored in the array using this loop, but we can access them. If we want to change them, we should use a standard For loop to iterate through the indices of the array: