| 1 |
Constructor |
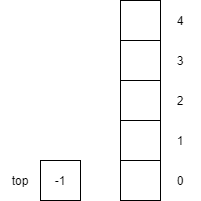
Creates an empty stack.

|
| 2 |
isFull() |
Returns false since top is not equal to the capacity of the stack.


|
| 3 |
isEmpty() |
Returns true since top is equal to -1


|
| 4 |
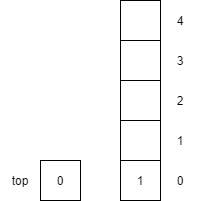
push(1) |
Increments top by 1 and then places item $1$ onto the top of the stack

|
| 5 |
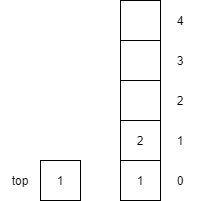
push(2) |
Increments top by 1 and then places item $2$ onto the top of the stack

|
| 6 |
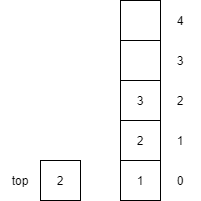
push(3) |
Increments top by 1 and then places item $3$ onto the top of the stack

|
| 7 |
peek() |
Returns the item $3$ on the top of the stack but does not remove the item from the stack. top is unaffected by peek


|
| 8 |
pop() |
Returns the item $3$ from the top of the stack and removes the item from the stack. top is decremented by 1.


|
| 9 |
pop() |
Returns the item $2$ from the top of the stack and removes the item from the stack. top is decremented by 1.


|
| 10 |
pop() |
Returns the item $1$ from the top of the stack and removes the item from the stack. top is decremented by 1.


|
| 11 |
isEmpty() |
Returns true since top is equal to -1


|