Variable Roles
Variables in our programs can be used in a variety of different roles. The simplest role for any variable is to store a value that does not change throughout the entire program. Most variables, however, fit into one of several roles throughout the program.
To help us understand these roles, let’s review them in detail here. As we move forward in this course, we’ll see many different data structures that use variables in these ways, so it helps to know each of them early on!
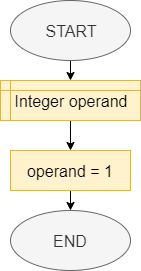
Container
In this role, the variable is used to hold a value. This value can be changed during the program execution. In the example:
- a variable named
operandof type Integer is declared - the value 1 is assigned to the variable
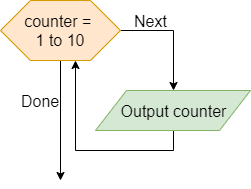
Counter
In this role, variables are used to hold a sequence of values known beforehand. In the example, the variable counter holds values from 1 to 10 and these values are conveyed to the user.
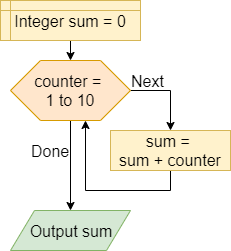
Accumulator
In this role, the variable is used to hold a value that aggregates, summarizes, and synthesize multiple values by means of an operation such as sum, product, mean, geometric mean, or median. In the example, we calculate the sum of the first ten numbers in the accumulator variable sum.
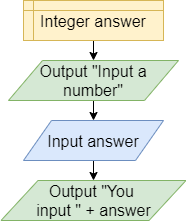
Recent Value
In this role, the variable answer contains the last value encountered so far in a data series, such as the last value that the program receives from the user.
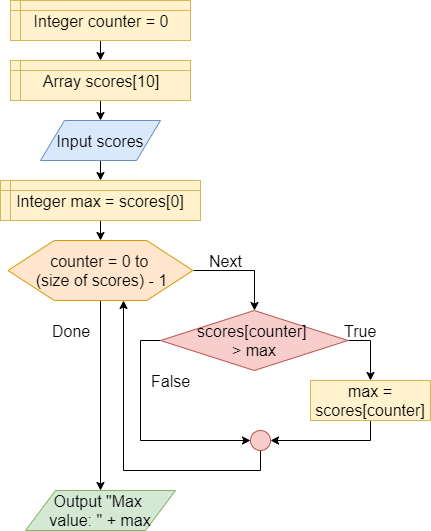
Extreme Value
In this role, the variable contains the value that is most appropriate for the purpose of the program, e.g. the minimum or the maximum. The instruction scores[counter] > max checks if the list item under observation is greater than the maximum. If the condition is true the value of the maximum variable is changed.
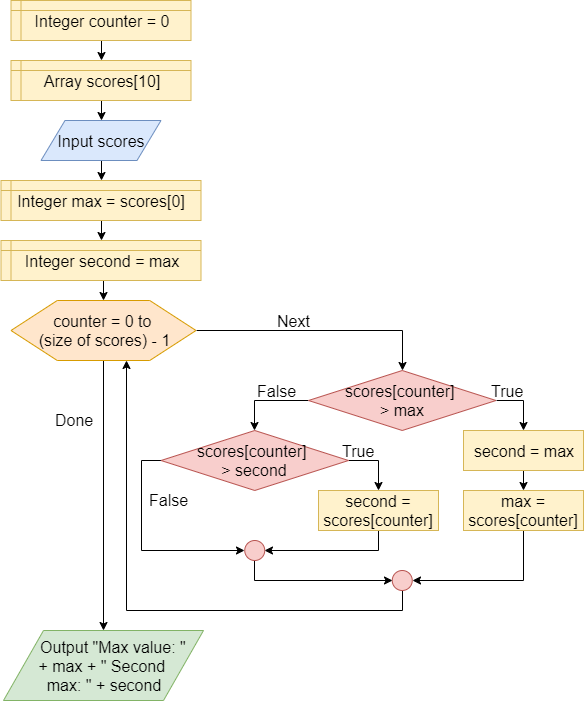
Follower
A variable, such as second, to which you assign the value of another variable that will be changed immediately after. In the example, the second variable contains the second largest value in a list.
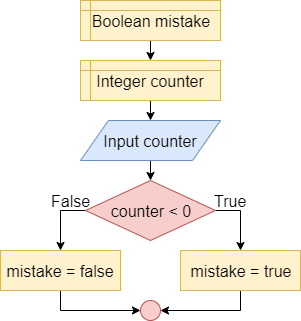
Flag
A flag variable is used to report the occurrence or not of a particular condition, e.g. the occurrence of an error, the first execution, etc..
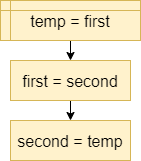
Temporary
A variable used to hold a temporary value. For example, to exchange two variables, you must have a temporary variable temp to store a value before it is replaced.
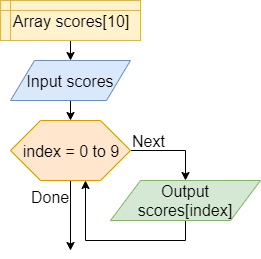
Index
A variable used to indicate the position of the current item in a set of elements, such as the current item in an array of elements. The index variable here is a great example.
References
- Sajaniemi, J. (2005, October). Roles of variables and learning to program. In Proc. 3rd Panhellenic Conf. Didactics of Informatics, Jimoyiannis A (ed) University of Peloponnese, Korinthos, Greece.
- Hosanee, M., & Rana, M. E. (2018). A Refined Approach for Understanding Role of Variables in Elementary Programming. Jour of Adv Research in Dynamical & Control Systems, 10(11).