Selection Sort
The first sorting algorithm we’ll learn about is selection sort. The basic idea behind selection sort is to search for the minimum value in the whole container, and place it in the first index. Then, repeat the process for the second smallest value and the second index, and so on until the container is sorted.
Wikipedia includes a great animation that shows this process:
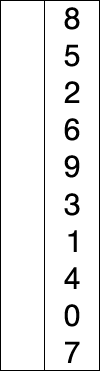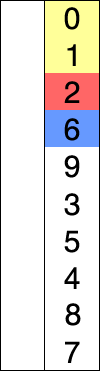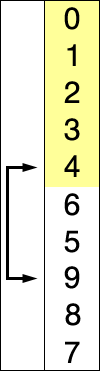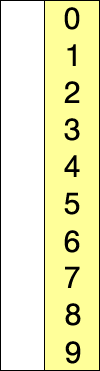
 ^[File:Selection-Sort-Animation.gif. (2016, February 12). Wikimedia Commons, the free media repository. Retrieved 22:22, March 23, 2020 from https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:Selection-Sort-Animation.gif&oldid=187411773.]
^[File:Selection-Sort-Animation.gif. (2016, February 12). Wikimedia Commons, the free media repository. Retrieved 22:22, March 23, 2020 from https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:Selection-Sort-Animation.gif&oldid=187411773.]
In this animation, the element highlighted in blue is the element currently being considered. The red element shows the value that is the minimum value considered, and the yellow elements are the sorted portion of the list.
Selection Sort Example
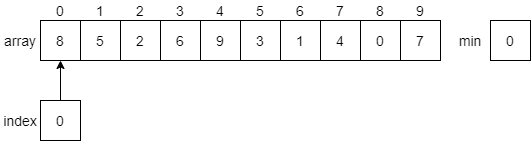
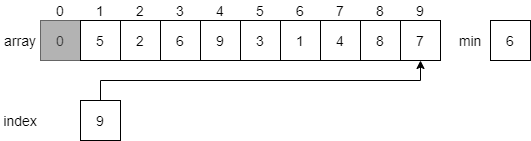
Let’s look at a few steps in this process to see how it works. First, the algorithm will search through the array to find the minimum value. It will start by looking at index 0 as shown in the figure below.
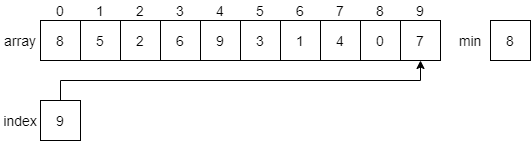
Once it reaches the end of the array, it will find that the smallest value 0 is at index 8.
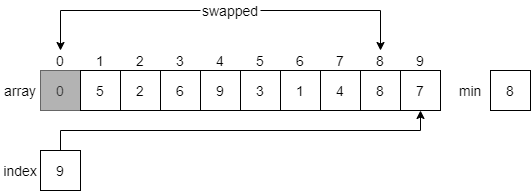
Then, it will swap the minimum item with the item at index 0 of the array, placing the smallest item first. That item will now be part of the sorted array, so we’ll shade it in since we don’t want to move it again.
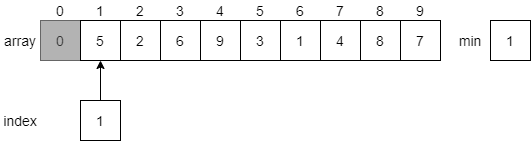
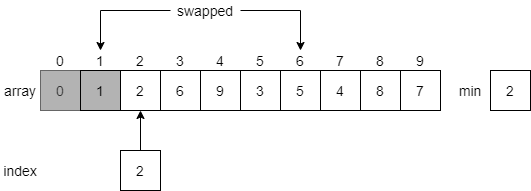
Next, it will reset index to 1, and start searching for the next smallest element in the array. Notice that this time it will not look at the element at index 0, which is part of the sorted array. Each time the algorithm resets, it will start looking at the element directly after the sorted portion of the array.
Once again, it will search through the array to find the smallest value, which will be the value 1 at index 6.
Then, it will swap the element at index 1 with the minimum element, this time at index 6. Just like before, we’ll shade in the first element since it is now part of the sorted list, and reset the index to begin at index 2
This process will repeat until the entire array is sorted in ascending order.