Mocks
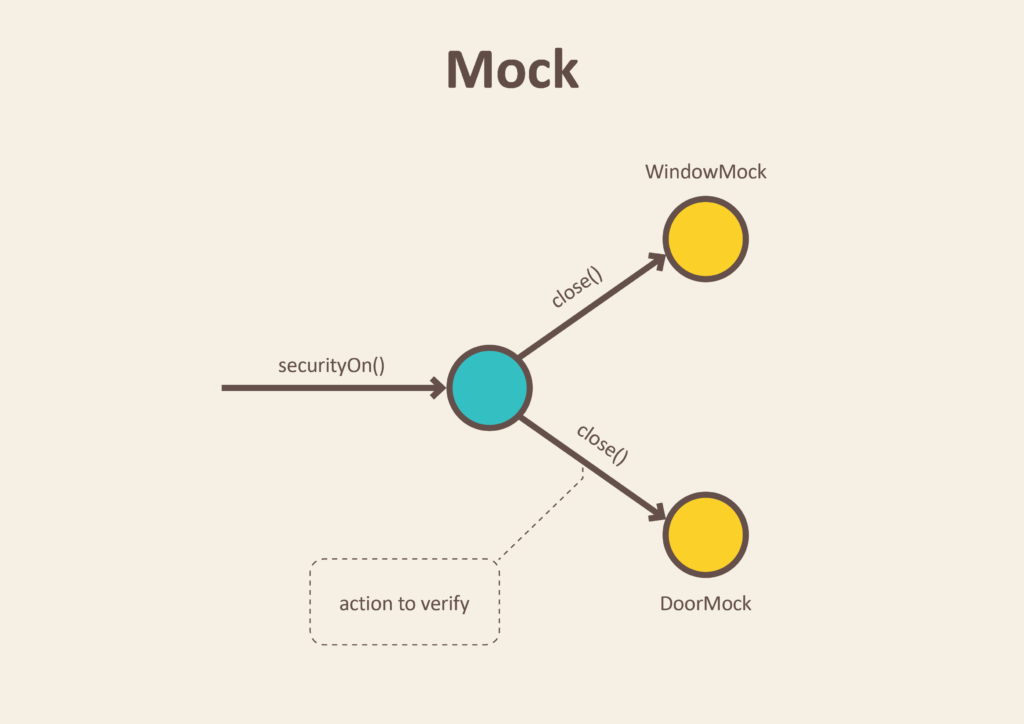
The third type of test double we’ll cover is the mock object, sometimes referred to as a test spy. A mock object is typically used to verify that our code performs the correct actions on other parts of the system. Usually, the mock object will simply listen for any incoming method calls, and then once our action is complete we can verify that the correct methods were called with the correct inputs by examining our mock object.
For example, if the code we are testing is responsible for calling a method in another module to update the GUI for our application, we can replace that GUI with a mock object, run the code, and then verify that the correct method in our mock object was called during the test. Likewise, we can make sure that other methods were not called.
This is another great example of an “indirect output” of our code. However, instead of data being the output, the messages sent as method calls are the data that our code is producing.
As we can see, test doubles are powerful tools we can use to enhance our ability to perform unit tests on our system. On the following pages, we’ll briefly review how to use different test doubles in both Java and Python. As always, feel free to skip to the page for the language you are learning, but both pages may contain helpful information.